Gum & Periodontal Disease:
Gum disease is caused by bacterial plaque deposited on teeth. It results in bleeding gums, sensitivity, bad smell, periodontal pocketing, gum recession, bone loss and tooth mobility. Periodontitis is common and usually is the result of poor oral hygiene. Brushing at least twice a day, flossing daily and getting regular dental checkups, scaling and polishing can prevent from periodontal diseases.
Symptoms:
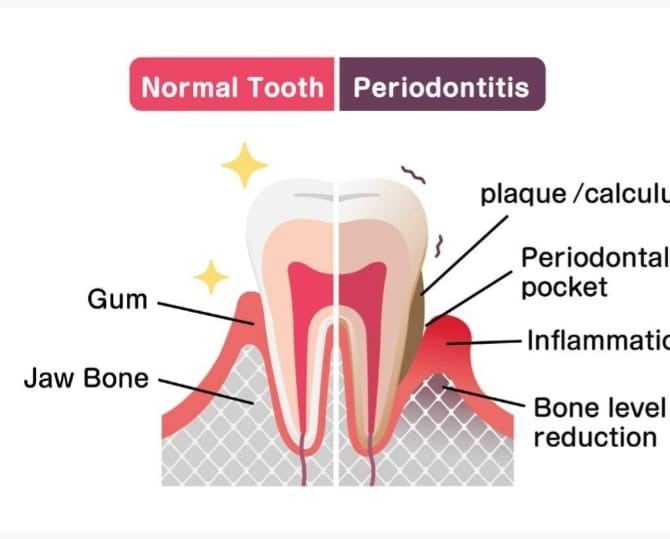
Healthy gums are firm and pale pink and fit snugly around teeth. Signs and symptoms of periodontitis can include:
- Swollen gums that bleed easily.
- Bright red or dusky red or purplish gums due to inflammation.
- Gums pain and tenderness when touched.
- Gums that bleed easily while eating, brushing etc.
- Pink-tinged toothbrush after brushing.
- Bad breath or oral malodor.
- Pus and abscess formation between the teeth and gums.
- Tooth mobility.
- Pain and difficulty in chewing.
- New spaces developing between teeth and pathological tooth movement and drifting.
- Gums recession, making your teeth look longer than normal.
- Periodontal pocketing and bleeding on probing.
- Bone loss on radiograph.
When to see a dentist?
Follow six-month dentist’s recommended schedule for regular checkups. If you notice any symptoms of periodontitis, make an appointment with dentist to early diagnose disease. Early diagnosis is key for successful prevention of disease and treatment.
Causes:
- Plaque (Biofilm): It is organized layers of bacteria deposited on tooth surface. Bacteria deposited as plaque (biofilm) are main factors contributing to disease.
- Plaque calcified into tartar (calculus): Calculus is a calcified deposit on teeth surface. Plaque contributes to calculus formation and calculus promotes the plaque formation on tooth surface.
- Plaque cause gingivitis: Gingivitis is inflammation of gum disease characterized by gum bleeding. There is no periodontal pocketing and bone loss. Gingivitis can be reversed with professional treatment (Scaling and polishing) and good home oral care.
- Gingivitis contributes to periodontitis: Periodontitis is damage of periodontal structure resulting in periodontal pocketing, periodontal attachment loss and bone loss and ultimately tooth mobility and tooth loss.
Risk factor for periodontitis:
Factors that can increase your risk of periodontitis include:
- Plaque and Calculus are main factors for periodontitis. Following factors do contribute as well.
- Gingivitis
- Poor oral hygiene and irregular brushing habits.
- Hormonal fluctuation e.g., puberty, disturbed menstrual cycle, pregnancy and menopause.
- Nutrition deficiencies especially vitamin C deficiency.
- Genetics Factors.
- Immune system deficiency: leukemia, HIV/AIDS.
- Systemic disease such as diabetes, arthritis.
Complications:
- Periodontitis cause bone loss with resulting tooth mobility and tooth loss.
- Systemic Disease: The bacteria enter into blood through inflamed gum tissue and are contributory factors for systemic disease. For example, periodontitis is linked with respiratory disease, rheumatoid arthritis, coronary artery disease (angina, myocardial infarction) and diabetes.
Prevention and Treatment:
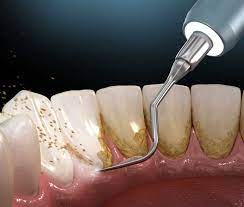
The best way to prevent and treat periodontitis is by removing dental plaque and calculus from teeth.
-
- Good oral hygiene: Brushing twice a day and flossing at least once a day is recommended for successful prevention and treatment of periodontal disease.
- Regular dental visits: Scaling and polishing every 6 to 12 months is key to success for managing periodontal disease.
- Controlling medical disease: Medical conditions like diabetes mellitus, bone disease like arthritis exuberate the periodontal disease. Medical disease management by physician is needed to control gum disease.
- Host modulation: Overstimulated immune system also contributes gum disease. In patient with aggressive periodontitis, immune system modulation by host modulation therapy is key to success control disease. Periostat uses 20 mg doxycycline twice daily for period of 3 to 9 months. It prevents gum breakdown from immune system.

Periodontal Surgery: Gingivectomy and Periodontal surgical therapy is used in severe cases for excellent cleaning of root surface and deep periodontal pocketing reduction. Periodontal flap is raised to directly access root surface.
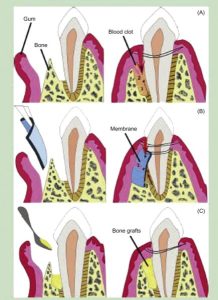
 Guided Tissue Regeneration (GBR): It is used to regenerate lost bone and periodontal structure. A barrier membrane is place between gum and periodontal tissue. Rapid growing epithelium and gum tissue is prevented from growing into periodontal tissue by membrane. This allows slowly growing periodontal tissue to regenerate periodontal structure.
Guided Tissue Regeneration (GBR): It is used to regenerate lost bone and periodontal structure. A barrier membrane is place between gum and periodontal tissue. Rapid growing epithelium and gum tissue is prevented from growing into periodontal tissue by membrane. This allows slowly growing periodontal tissue to regenerate periodontal structure.

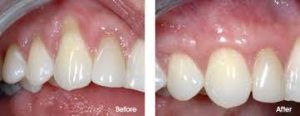
- Periodontal Plastics Surgery: Periodontal plastic surgery procedures like free gingival graft are used for reconstruction of papilla, gum recession treatment and increasing depth of keratinized tissue.



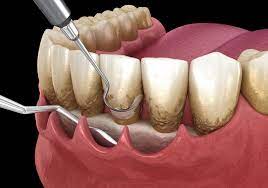 Guided Tissue Regeneration (GBR): It is used to regenerate lost bone and periodontal structure. A barrier membrane is place between gum and periodontal tissue. Rapid growing epithelium and gum tissue is prevented from growing into periodontal tissue by membrane. This allows slowly growing periodontal tissue to regenerate periodontal structure.
Guided Tissue Regeneration (GBR): It is used to regenerate lost bone and periodontal structure. A barrier membrane is place between gum and periodontal tissue. Rapid growing epithelium and gum tissue is prevented from growing into periodontal tissue by membrane. This allows slowly growing periodontal tissue to regenerate periodontal structure.